Can we help you?
Contact us

Can we help you?
Contact us

Thank you for contacting us
Your form has been submitted successfully Our team will contact you again as soon as possible.
Whooppss...!! An error has occurred
Try sending later or write an email directly to areaempresas@ua.es

INFO
SHEET
DOWNLOAD
EXECUTIVE
ABSTRACT
CONTACT DETAILS: Research Results Transfer Office-OTRI
University of Alicante
Tel.: +34 96 590 99 59
Email: areaempresas@ua.es
http://innoua.ua.es
The know-how involves the ability to measure a very low concentration of dioxins (values close to picograms or femtograms). The technique also permits the quantitative analysis of almost all the congeners of dioxins and furans (more than 130 different compounds), not only the main 17 toxic compounds.

Dioxin is one of the most toxic chemicals known. A draft report released for public comment in 2000 by the US Environmental Protection Agency clearly describes dioxin as a serious public health threat. According to the EPA report, not only does there appear to be no "safe" level of exposure to dioxin, but levels of dioxin and dioxin-like chemicals have been found in the general US population that are "at or near levels associated with adverse health effects." The EPA report confirmed that dioxin is a cancer hazard to people; that exposure to dioxin can also cause severe reproductive and developmental problems (at levels 100 times lower than those associated with its cancer causing effects); and that dioxin can cause immune system damage and interfere with regulatory hormones.
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. 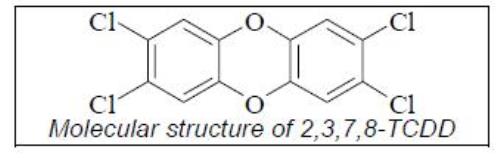
Dioxins are non-biodegradable chemicals. Due to this, dioxins are accumulated in the tissues of the living creatures, mainly in the fatty materials. In this way, we can find the major concentration in the fish fat, meat fat or in the milk (human or animal milk). Various sources indicate that the thermal processes are the responsible for the major contribution of dioxins to the environment.
The know-how involves the ability to measure a very low concentration of dioxins (values close to picograms or femtograms). It does not depend on the precise equipment but the expertise in preparing properly the samples by means of a very sensitive and specific analytical method.
The technique also permits the quantitative analysis of almost all the congeners of dioxins and furans (more than 130 different compounds), not only the main 17 toxic compounds.
Nowadays, this methodology (standard one) is the only one available method to carry out reliable dioxin analyses.
The method has been tested in our laboratory for the determination of all the congeners of dioxins and furans in water, soil, sediment, sludge, fish, milk, combustion gases, ash and used oils, although the procedure can be applied to several other matrices.
The technique could be applied to different fields:
- Control of gaseous emissions from the combustion of urban or industrial wastes. Following European directive 94/67/CE of the Council, related to the incineration of hazardous wastes, the emission limit is 0.1ng/Nm3.
- Characterization of hazardous and toxic wastes. The directive of the European Council establish a content of dioxins lower than 0.01 % for the waste to be considered hazardous and toxic.
- Determination in food and feed (milk and derivates, meat, fish,…). It is estimated that more than 90 % of the environmental exposure to dioxins and furans is trough the food, specially those of animal origin. In theindustrialized countries the averages daily ingest of PCDD/Fs is 50-200 pg/person/day.
- Determination in sewage sludges and other organic fertilizers (therefore in composting plants). It exists a draft for a normative referring to the limit of dioxins and furans of 100 ng/kg dry solid.
- Determination in other matrices such as tissues and blood, air, emission due to the trafic, paper, ink, higienic materials, tobacco smoke, chimney soot, dust…
Two types of cooperation are sought by the Department of Chemical Engineering of the University of Alicante:
• Accomplishment of the extraction, cleanup and analysis of dioxins and related compounds to samples that companies are interested in.
• Instruct people interested in perform the tasks involved in the dioxin analysis, with training courses designed specifically for each situation.
The Department of Chemical Engineering owns the know-how to carry out the dioxin and furan extraction, cleanup and analysis. Protection by patent is not applicable.
Materials and Nanotechnology
Chemical Technology
Carretera San Vicente del Raspeig s/n - 03690 San Vicente del Raspeig - Alicante
Tel.: (+34) 965 90 9959




