Can we help you?
Contact us

Can we help you?
Contact us

Thank you for contacting us
Your form has been submitted successfully Our team will contact you again as soon as possible.
Whooppss...!! An error has occurred
Try sending later or write an email directly to areaempresas@ua.es

INFO
SHEET
DOWNLOAD
EXECUTIVE
ABSTRACT
CONTACT DETAILS: Research Results Transfer Office-OTRI
University of Alicante
Tel.: +34 96 590 99 59
Email: areaempresas@ua.es
http://innoua.ua.es
A Spanish Research Group has developed a system to help in the recognition of a melanoma through the visual characteristics of an image of the skin lesion. This system can be used as an automated way to decide the urgency to refer a patient to the dermatologist.

The melanoma is a type of skin cancer very aggressive and with a high incidence in many countries like Australia, USA or European Mediterranean countries; unfortunately, each year the number of patients is increasing. In spite of the aggressiveness of this kind of cancer, if it is removed in early phases, the results for the patients are very good. Otherwise, if it is not diagnosed in early phases the life expectance is reduced considerably. Therefore it is fundamental to diagnose as soon as possible a skin lesion and to distinguish a melanoma from benign lesions (a simple spot or a mole). Dermatologists encourage people to self-exploring and to go to doctor if they observe a suspected skin lesion or if it is changed in a period of time.
To identify a melanoma, dermatologists use several techniques which have been developed based on experience. All these techniques allow identifying symptoms of a malignant lesion based on the observation of a series of characteristics. It is important to bear in mind that the diagnosis of a melanoma through the visual interpretation of the characteristics of the lesion is a difficult task.
The Spanish Research Group has developed a system to help in the recognition of a melanoma through the visual characteristics of an image of the skin lesion. This system can be used as an automated way to decide the urgency to refer a patient to the dermatologist.
The decision support system for melanoma diagnosis studied has three phases: first, a preprocessing of the images which includes the segmentation process; next, the selection of characteristics used to classify the image; finally, the classification of the lesion.
In the preprocessing phase, the system carries out some tasks to prepare the image to be analysed. All the digital images have impulse noise which can be reduced applying a filter. Another task of the preprocessing phase is the segmentation. The objective is to split objects of the scenario to get just the lesion area from the image.
For the selection of characteristics, the software is based on the ABCD rule (Asymmetry, Border, Colour, Diameter). It obtains a set of characteristics divided into three groups: one related to the shape, other to the border and the last one to the colour. The software developed use a selection of the set of characteristics that gives the best results.
The last phase of the system is the classification of the images in two classes: benign lesions or melanoma. For the final classification the software uses the combination of several independent classifiers. The classification rates for the system are higher than 90%. This can be incremented by using it because this system can self-learn.
This software is fully developed and available for demonstration. The researchers are looking for medical services that trained and, after, validate this software with dermatoscopic images and companies acquiring this technology for exploitation, although the group is open to other kind of collaboration.
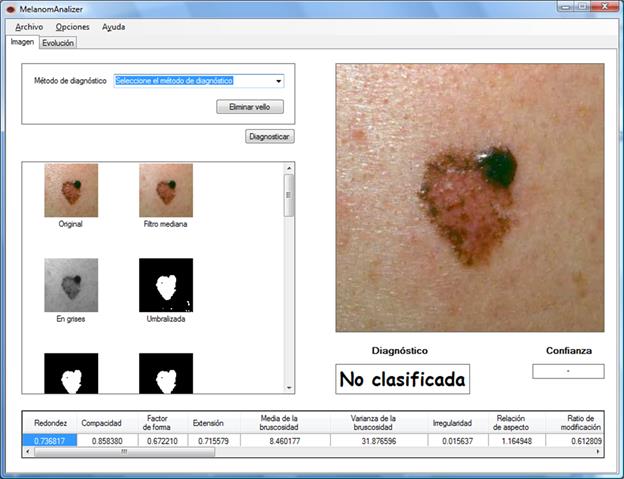
Image 1: Screen print of the software for melanoma diagnosis
- Costs reduction of melanoma campaigns. Clinical staff can capture the photographs of the lesion and then, the system decides the urgency to be analyzed by a specialist.
- Several diagnosis proposed by artificial entities are combined to obtain a more accurate diagnosis.
INNOVATIVE ASPECTS
- The system has been developed using web technologies so its integration to teledermatology is direct.
- System is learning continuously so as much is used, better the results will be. The system efficiency increases with the use because it can learn by itself as an expert system and neuronal network.
Available for demonstration
- Clinical diagnosis on Dermatology
The software described is an expert system that can help to the doctor for melanoma diagnosis.
This system can be applied in the detection of other diseases which are diagnosed by image analysis.
- Type of partner sought: Private companies
- Specific area of activity of the partner: Software for health and diagnosis or Software for processing images
- Task to be performed: Acquire the technology for its commercial exploitation. The research group is also open to other kind of collaboration (For example: R&D new application of this technology for the diagnosis of other diseases, application of this technology in other fields, as quality control, control processing, etc.)
The system is protected by Intellectual Property Rights under copyright.
Carretera San Vicente del Raspeig s/n - 03690 San Vicente del Raspeig - Alicante
Tel.: (+34) 965 90 9959





